http://www.spoj.com/problems/ETF/
Is there an O(N) method to calculate phi functions of all the numbers from 1 to N? I swear, i saw a post here on codeforces about it, but i just can't seem to find it.
Anyway i used the fact that 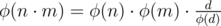 where d = gcd(n, m) + a sieve to solve the above problem in
where d = gcd(n, m) + a sieve to solve the above problem in 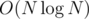 , is it possible to do it in O(N)?
, is it possible to do it in O(N)?











Thanks a lot dude I used your technique for various problems involving totient functions
Do you know how to find the smallest prime divisor of each number in O(N)? If don't, please read this (in Russian, but Google Translate works well).
But if you know the smallest prime divisor, the solution is easy. You just need to precalculate the power of this factor and use it for phi calculation. If something is still unclear, please look at this pseudocode:
UPD. Oh, I didn't notice the comment above.
if(Smallest_Prime[i]==0) Phi[i]=i-1I get this part. If i is a prime number then Phi[i] must be i-1 (As all the number from 1..to i-1 are relative prime to i ).
But I am confused with this part
Let i = 8, then according to the code blocked above,
if(lp[i] == lp[ i/lp[i] ])this part is true (As lp[8] == 2 and lp[4] == 2 also ) then we are puttingphi[i] = phi[i / lp[i]] * lp[i];What is the prof of that?Please Someone help .. Thank You :)
You can get it from the formula for PHI:
PHI [n] = n * (1 - 1/p1) * (1 - 1/p2) * ... * (1 - 1/pn)where p1,p2.. pn are the prime factors of n.Say we know the smallest prime factor of n, that is lp [n]. What is the formula for n/lp[n] ? Well there are two cases:
1) n/lp[n] is still divisible by lp[n], that is lp[n] is a factor of n with a power greater than or equal to 2, so n/lp[n] has exactly the same prime factors as n.
Then PHI[n/lp[n]] = (n/lp[n]) * (1 - 1/p1) * (1 - 1/p2) * ... * (1 - 1/pn)It differs from the above formula by the first term. So just multiply phi[n/lp[n]] by lp[n] to get phi[n].PHI[n] = PHI[n/lp[n]] * lp[n]2) n/lp[n] is not divisible by lp[n], then the above formula for n/lp[n] is almost the same, it just doesn't have (1 — 1/lp[n]) as one of its terms. So we have to multiply phi[n/lp[n]] not only by lp[n] but also by (1 — 1/lp[n]).
Then PHI[n] = PHI[n/lp[n]] * lp[n] * (1 - 1/lp[n]] => PHI[n] = PHI[n/lp[n]] * (lp[n] - 1)These are exactly the two cases in savinov's if-else statement in the code above.
Sorry for the bad editing. This is my first comment.
Thanks Mikester and savinov , Your explanations helped a lot :)
Using the fact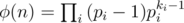 you can obtain it by simple calculations. Try to understand when we take into account some prime at first time.
you can obtain it by simple calculations. Try to understand when we take into account some prime at first time.