Introduction
When we are working with pointers and trees it is difficult for us to visualise what is going on inside. We will create a function template which will take root as the input and plot the tree beautifully. You can give root of any tree like AVL tree, BST, Splay tree, etc. But make sure that it has at least following attributes -
struct Node
{
int data; // value
struct Node *left, *right; //left child, right child
};
There are two files -
- printer.h — utility function template
- test.cpp — driver programme
Since printing the trees require space, it is not possible to print a tree with height more than 5 on portable computer screen. This programme is helpful for debugging your trees but it cannot accommodate more than height of 5.
Implementation
// printer.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// returns the number of spaces needed for writing the numbers
int digitCount(int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (n)
{
cnt++;
n /= 10;
}
return cnt;
}
// accepts a tree class
template <typename T>
void printer(T *root)
{
cout << "\n\n";
// calculating maximum depth of the tree and assigning parent
// to each node
map<T*,T*> parent;
map<int,int> dist;
vector<T *> mp[200];
queue<T *> q;
int maxdepth = 0;
q.push(root);
dist[root->data] = 0;
mp[0].push_back(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
T *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curr->left != 0)
{
parent[curr->left] = curr;
q.push(curr->left);
dist[curr->left->data] = dist[(curr->data)] + 1;
mp[dist[curr->left->data]].push_back(curr->left);
maxdepth = max(maxdepth, dist[curr->left->data]);
}
if (curr->right != 0)
{
parent[curr->right] = curr;
q.push(curr->right);
dist[curr->right->data] = dist[curr->data] + 1;
mp[dist[curr->right->data]].push_back(curr->right);
maxdepth = max(maxdepth, dist[curr->right->data]);
}
}
// maximum depth calculation ends
// printing the root on the middle of the screen
printf("%72d\n\n", root->data);
// -> hashing for visited nodes
// -> offset denotes the count of spaces from the left end of the screen
// for a node
map<int,int> hashing, offset;
offset[root->data] = 70;
hashing[root->data] = 1;
// k decides the width of the branch to be taken for printing the numbers at each level
int k = 2;
// since it is a binary tree we will start with k = 2^maxdepth and keep
// reducing it by a factor of 2 at each level
for (int i=0;i<maxdepth;i++) k*=2;
for (int i = 1; i <= maxdepth; i++, k/=2)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (auto z : mp[i])
{
if (hashing[z->data])
continue;
while (cnt < offset[parent[z]->data] - k)
{
cout << ' ';
cnt++;
}
// for left node
if (parent[z]->left != 0)
{
offset[z->data] = cnt;
cout << (z->data);
cnt += digitCount(z->data);
hashing[z->data] = 1;
while (cnt < offset[parent[z]->data])
{
cnt++;
cout << '_';
}
cout << '|';
cnt++;
}
// for right node
if (parent[z]->right != 0)
{
if (parent[z]->left == 0)
{
while (cnt < offset[parent[z]->data])
{
cnt++;
cout << ' ';
}
cout << '|';
cnt++;
}
offset[parent[z]->right->data] = offset[parent[z]->data] - 2 + k ;
while (cnt < offset[parent[z]->right->data])
{
cnt++;
cout << '_';
}
cout << parent[z]->right->data;
cnt += digitCount(parent[z]->right->data);
hashing[parent[z]->right->data] = 1;
}
}
cout << "\n\n";
k--;
}
cout << "\n\n\n";
}
Demonstration
// test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "printer.h"
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
class Node *left, *right;
int data;
Node *create(int value)
{
Node *newnode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newnode->data = value;
newnode->left = 0;
newnode->right = 0;
return newnode;
}
};
int main()
{
Node *head, *one, *two, *three, *four, *five, *six
, *seven, *eight, *nine;
// creating nodes
head = (new Node())->create(30);
one = (new Node())->create(4);
two = (new Node())->create(7);
three = (new Node())->create(8);
four = (new Node())->create(0);
five = (new Node())->create(29);
six = (new Node())->create(-993);
seven = (new Node())->create(345);
eight = (new Node())->create(-3433);
nine = (new Node())->create(888);
// linking nodes
head->left = one;
head->right = two;
one->left = three;
one->right = four;
two->left = five;
two->right = six;
four->left = seven;
four->right = eight;
seven->left = nine;
printer<Node>(head);
return 0;
}
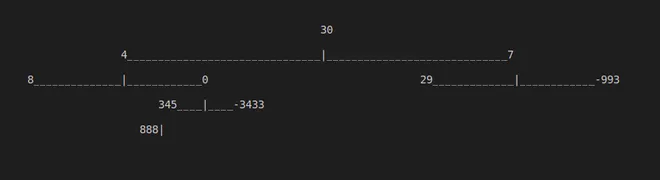
Output