Разбор задач Hello 2018 доступен на русском и английском языках. Приятного прочтения!
Возведение в степень по модулю
Автор задачи: tourist
Tutorial is loading...
Код
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
printf("%d\n", n >= 31 ? m : m % (1 << n));
return 0;
}
Новогодняя елка
Автор задачи: budalnik
Tutorial is loading...
Код на C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> p(n), deg(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i];
p[i]--;
deg[p[i]]++;
}
vector<int> sons_leaves(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (deg[i] == 0) {
sons_leaves[p[i]]++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (deg[i] > 0 && sons_leaves[i] < 3) {
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
puts("Yes");
return 0;
}
Код на Python
n = int(input())
p = [int(input()) - 1 for _ in range(n - 1)]
leafs = list(filter(lambda x: not x in p, range(n)))
lp = [x for i, x in enumerate(p) if i + 1 in leafs]
x = min(lp.count(k) for k in p)
print("Yes" if x >= 3 else "No")
Лимонад для вечеринки
Автор задачи: tourist
Tutorial is loading...
Код
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, L;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &L);
vector<int> c(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
c[i + 1] = min(c[i + 1], 2 * c[i]);
}
long long ans = (long long) 4e18;
long long sum = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int need = L / (1 << i);
sum += (long long) need * c[i];
L -= need << i;
ans = min(ans, sum + (L > 0) * c[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Слишком простые задачи
Автор задачи: tourist
Tutorial is loading...
Решение с бинарным поиском
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, T;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &T);
vector<int> a(n), t(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &a[i], &t[i]);
}
vector<int> res;
int low = 0, high = n;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high + 1) >> 1;
vector< pair<int,int> > e;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] >= mid) {
e.emplace_back(t[i], i);
}
}
sort(e.begin(), e.end());
bool ok = false;
if ((int) e.size() >= mid) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) {
sum += e[i].first;
}
if (sum <= T) {
ok = true;
res.resize(mid);
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) {
res[i] = e[i].second;
}
}
}
if (ok) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
int sz = (int) res.size();
printf("%d\n%d\n", sz, sz);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
putchar(' ');
}
printf("%d", res[i] + 1);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Решение с set
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, T;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &T);
vector< vector< pair<int, int> > > at(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int foo, bar;
scanf("%d %d", &foo, &bar);
at[foo].emplace_back(bar, i);
}
vector<int> res;
set< pair<int, int> > s;
int sum = 0;
for (int k = n; k > 0; k--) {
for (auto &p : at[k]) {
sum += p.first;
s.emplace(p);
}
while ((int) s.size() > k) {
sum -= (--s.end())->first;
s.erase(--s.end());
}
if ((int) s.size() == k && sum <= T) {
for (auto &p : s) {
res.push_back(p.second);
}
break;
}
}
int sz = (int) res.size();
printf("%d\n%d\n", sz, sz);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
putchar(' ');
}
printf("%d", res[i] + 1);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Логическое выражение
Автор задачи: budalnik
Tutorial is loading...
Код 1
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool ls(const string& a, const string& b) {
if (a.length() == b.length()) return a < b;
return a.length() < b.length();
}
struct Expression {
int p, t;
string e;
Expression(string _e, int t_, int _p) : e(_e), t(t_), p(_p) {}
bool operator < (const Expression& ex) const {
if (ex.e == e) {
if (t != ex.t) {
return t < ex.t;
}
return p < ex.p;
}
return ls(e, ex.e);
}
};
set<Expression> q;
const int FULL = 0xff;
const vector<int> B = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128};
const int X_TABLE = B[4] + B[5] + B[6] + B[7];
const int Y_TABLE = B[2] + B[3] + B[6] + B[7];
const int Z_TABLE = B[1] + B[3] + B[5] + B[7];
string dp[1 << 8][3];
void add(int pr, const string& s, int mask) {
if (dp[mask][pr].empty() || ls(s, dp[mask][pr])) {
dp[mask][pr] = s;
Expression e(s, mask, pr);
q.insert(e);
}
}
int main() {
add(2, "x", X_TABLE);
add(2, "y", Y_TABLE);
add(2, "z", Z_TABLE);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto e = *q.begin();
q.erase(q.begin());
if (e.p == 2) {
add(2, "!" + e.e, ~e.t & FULL);
add(1, e.e, e.t);
}
if (e.p == 1) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < FULL; ++mask) {
if (!dp[mask][2].empty()) {
add(1, dp[mask][2] + "&" + e.e, mask & e.t);
add(1, e.e + "&" + dp[mask][2], mask & e.t);
}
}
add(2, "(" + e.e + ")", e.t);
add(0, e.e, e.t);
}
if (e.p == 0) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < FULL; ++mask) {
for (int pr = 1; pr <= 2; ++pr) {
if (!dp[mask][pr].empty()) {
add(0, dp[mask][pr] + "|" + e.e, mask | e.t);
add(0, e.e + "|" + dp[mask][pr], mask | e.t);
}
}
}
add(2, "(" + e.e + ")", e.t);
}
}
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
string s;
cin >> s;
int mask = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
if (s[i] == '1') {
mask |= (1 << i);
}
}
cout << dp[mask][0] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Код 2
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string res[256][3];
bool changed;
void update(string &a, string &b) {
if (a == "" || (b.length() < a.length() || (b.length() == a.length() && b < a))) {
changed = true;
a = b;
}
}
int main() {
res[(1 << 4) + (1 << 5) + (1 << 6) + (1 << 7)][0] = "x";
res[(1 << 2) + (1 << 3) + (1 << 6) + (1 << 7)][0] = "y";
res[(1 << 1) + (1 << 3) + (1 << 5) + (1 << 7)][0] = "z";
changed = true;
while (changed) {
changed = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (res[i][j] == "") {
continue;
}
{ // op == 0
string s = res[i][j];
if (j > 0) {
s = "(" + s + ")";
}
s = "!" + s;
update(res[i ^ 255][0], s);
}
for (int ii = 0; ii < 256; ii++) {
for (int jj = 0; jj < 3; jj++) {
if (res[ii][jj] == "") {
continue;
}
for (int op = 1; op <= 2; op++) {
string s = res[i][j];
if (j > op) {
s = "(" + s + ")";
}
string t = res[ii][jj];
if (jj > op) {
t = "(" + t + ")";
}
string w = s + (op == 1 ? '&' : '|') + t;
update(res[op == 1 ? (i & ii) : (i | ii)][op], w);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int tt;
cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
string z;
cin >> z;
int mask = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
mask |= (z[i] - '0') << i;
}
string best = "";
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
update(best, res[mask][j]);
}
cout << best << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Сильносвязный турнир
Автор задачи: YakutovDmitriy
Tutorial is loading...
Код
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int md = 998244353;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) a -= md;
}
inline void sub(int &a, int b) {
a -= b;
if (a < 0) a += md;
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (int) ((long long) a * b % md);
}
inline int power(int a, long long b) {
int res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int inv(int a) {
return power(a, md - 2);
}
int main() {
int n, P, Q;
cin >> n >> P >> Q;
int p = mul(P, inv(Q));
vector< vector<int> > p_win(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
p_win[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
add(p_win[i + 1][j], mul(p_win[i][j], power(p, j)));
add(p_win[i + 1][j + 1], mul(p_win[i][j], power((1 - p + md) % md, i - j)));
}
}
vector<int> p_strong(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p_strong[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
sub(p_strong[i], mul(p_strong[j], p_win[i][j]));
}
}
vector<int> res(n + 1);
res[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
res[i] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
int coeff = mul(p_strong[j], p_win[i][j]);
int games = (res[j] + res[i - j]) % md;
add(games, j * (j - 1) / 2 + j * (i - j));
add(res[i], mul(coeff, games));
}
add(res[i], mul(i * (i - 1) / 2, p_strong[i]));
res[i] = mul(res[i], inv((1 - p_strong[i] + md) % md));
}
cout << res[n] << endl;
return 0;
}
Степенная подстрока
Автор задачи: YakutovDmitriy
Tutorial is loading...
Код на Python
def dlog(x, n):
bigMod = 5 ** n
ans = [None, 0, 1, 3, 2][x % 5]
val = 2 ** ans % bigMod
mod, phi = 5, 4
phiVal = 2 ** phi % bigMod
for i in range(2, n + 1):
nextMod = mod * 5
while val % nextMod != x % nextMod:
val = val * phiVal % bigMod
ans += phi
phi *= 5
phiVal = (phiVal *
phiVal % bigMod *
phiVal % bigMod *
phiVal % bigMod *
phiVal % bigMod)
mod = nextMod
return ans
def main():
inp = input()
n = len(inp)
a = int(inp)
for m in range(n + 1):
l = a * 10 ** m
x, mod = l, 2 ** (n + m)
if x % mod != 0:
x += mod - x % mod
if x % 5 == 0:
x += mod
if x < l + 10 ** m:
assert x % mod == 0 and x % 5 != 0
x = x // mod
mod = 5 ** (n + m)
print(n + m + dlog(x % mod, n + m))
return
assert False
if __name__ == '__main__':
cnt = int(input())
for i in range(cnt):
main()
Код на C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline long long mul(long long a, long long b, long long md) {
long long res = 0;
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res += a; if (res >= md) res -= md;
}
a += a; if (a >= md) a -= md;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline long long power(long long a, long long b, long long md) {
long long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res = mul(res, a, md);
}
a = mul(a, a, md);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int tt;
cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
long long a;
cin >> a;
int n = (int) to_string(a).length();
for (int m = 0; ; m++) {
long long b = (-a) & ((1LL << (n + m)) - 1);
if ((a + b) % 5 == 0) {
b += (1LL << (n + m));
}
if ((b == 0 && m == 0) || (int) to_string(b).length() <= m) {
long long c = (a + b) >> (n + m);
long long t = vector<long long>{-1, 0, 1, 3, 2}[c % 5];
long long p5 = 5;
for (int i = 1; i < n + m; i++) {
while (power(2, t, p5 * 5) != c % (p5 * 5)) {
t += p5 / 5 * 4;
}
p5 *= 5;
}
t += n + m;
cout << t << endl;
break;
}
a *= 10;
}
}
return 0;
}
Не превышай
Автор задачи: tourist
Tutorial is loading...
Код решения за O(n^5)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int md = 998244353;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) a -= md;
}
inline void sub(int &a, int b) {
a -= b;
if (a < 0) a += md;
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (int) ((long long) a * b % md);
}
inline int power(int a, long long b) {
int res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int inv(int a) {
return power(a, md - 2);
}
const int N = 77;
int C[N][N];
typedef vector<int> poly;
poly integrate(poly a) {
poly b = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < (int) a.size(); i++) {
b.push_back(mul(a[i], inv(i + 1)));
}
return b;
}
void sub(poly &a, poly b) {
while (a.size() < b.size()) {
a.push_back(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int) b.size(); i++) {
sub(a[i], b[i]);
}
}
poly plug(poly a, int delta) {
// a(x + delta)
poly b(a.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < (int) a.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
add(b[j], mul(a[i], mul(C[i][j], power(delta, i - j))));
}
}
return b;
}
int eval(poly a, int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = (int) a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res = mul(res, x);
add(res, a[i]);
}
return res;
}
const int COEFF = 1000000;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
C[i][j] = (j == 0 ? 1 : (i == 0 ? 0 : (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) % md));
}
}
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> x(n), fracs;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
double foo;
cin >> foo;
x[i] = (int) (foo * COEFF + 0.5);
fracs.push_back(x[i] % COEFF);
}
fracs.push_back(0);
sort(fracs.begin(), fracs.end());
fracs.resize(unique(fracs.begin(), fracs.end()) - fracs.begin());
int cnt = (int) fracs.size();
vector<int> point(n * cnt + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n * cnt; i++) {
point[i] = mul(i / cnt * COEFF + fracs[i % cnt], inv(COEFF));
}
vector<int> cut(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cut[i] = (int) (find(point.begin(), point.end(), mul(x[i], inv(COEFF))) - point.begin());
}
vector<poly> a(n * cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
a[i] = {i < min(cnt, cut[0]) ? 1 : 0};
}
for (int id = 1; id < n; id++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
a[i] = integrate(a[i]);
}
for (int i = n * cnt - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
sub(a[i][0], eval(a[i], point[i]));
for (int j = i - 1; j >= i - cnt && j >= 0; j--) {
add(a[i][0], eval(a[j], point[j + 1]));
if (j > i - cnt) {
sub(a[i][0], eval(a[j], point[j]));
} else {
sub(a[i], plug(a[i - cnt], md - 1));
}
}
}
for (int i = cut[id]; i < n * cnt; i++) {
a[i] = {0};
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
poly b = integrate(a[i]);
add(ans, eval(b, point[i + 1]));
sub(ans, eval(b, point[i]));
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
Код решения за O(n^4)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int md = 998244353;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) a -= md;
}
inline void sub(int &a, int b) {
a -= b;
if (a < 0) a += md;
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (int) ((long long) a * b % md);
}
inline int power(int a, long long b) {
int res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int inv(int a) {
return power(a, md - 2);
}
typedef vector<int> poly;
poly integrate(poly a) {
poly b = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < (int) a.size(); i++) {
b.push_back(mul(a[i], inv(i + 1)));
}
return b;
}
void sub(poly &a, poly b) {
while (a.size() < b.size()) {
a.push_back(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int) b.size(); i++) {
sub(a[i], b[i]);
}
}
int eval(poly a, int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = (int) a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res = mul(res, x);
add(res, a[i]);
}
return res;
}
const int COEFF = 1000000;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> x(n), fracs;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
double foo;
cin >> foo;
x[i] = (int) (foo * COEFF + 0.5);
fracs.push_back(x[i] % COEFF);
}
fracs.push_back(0);
sort(fracs.begin(), fracs.end());
fracs.resize(unique(fracs.begin(), fracs.end()) - fracs.begin());
int cnt = (int) fracs.size();
vector<int> point(n * cnt + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n * cnt; i++) {
point[i] = i / cnt * COEFF + fracs[i % cnt];
}
vector<int> cut(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cut[i] = (int) (find(point.begin(), point.end(), x[i]) - point.begin());
}
vector<int> sz(n * cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
sz[i] = mul((point[i + 1] - point[i] + md) % md, inv(COEFF));
}
vector<poly> a(n * cnt);
vector<int> sum(n * cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
a[i] = i < min(cnt, cut[0]) ? vector<int>{0, 1} : vector<int>{0};
sum[i] = a[i].size() == 1 ? 0 : sz[i];
}
for (int id = 1; id < n; id++) {
for (int i = n * cnt - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i >= cut[id]) {
a[i] = {0};
sum[i] = 0;
} else {
for (int j = i - 1; j >= i - cnt && j >= 0; j--) {
add(a[i][0], sum[j]);
}
if (i - cnt >= 0) {
sub(a[i], a[i - cnt]);
}
a[i] = integrate(a[i]);
sum[i] = eval(a[i], sz[i]);
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n * cnt; i++) {
add(ans, sum[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}










Not a single tutorial is available ? Only solutions ?
Sorry, the tutorials will be available shortly after the end of system testing.
Don't be sorry man. Forgive us for being stupid and not understanding you problems, sorry.
sag salam miresoone
I'm liking this new trend.
why did this code accepted for Problem A?
cin>>n>>m; int a=pow(2,n); cout<<m%a<<endl;
При n==1000000 ,выражение станет больше чем unsigned long long;
why this solution worked? cin>>n>>m; int a=pow(2,n); cout<<m%a<<endl; what about overflow?!
a will be -2147483648, but in the way C++ works with negative modulo it will work...
a could be any value, couldn't it? Depending on n. It's unlikely to be <= 10^8, but possible or not?
It varies depending on the PC architecture (32 or 64 bits), compiler and operating system, in my PC and in Codeforces custom invocation it has that value. For every n >= 31 it has the same value.
Even though it overflows the % operation is unsigned so the number remains big enough to work properly.
in c++ when a large double number ( larger than the receiver type ) is put into smaller receiver it automatically casts it to the largest possible number to be put in the receiver in this case INT_MAX so when a number is calculated % INT_MAX it will always give the number
Can you give a source for this information?
you can try it write down cout << (int)1e12 and write down cout << INT_MAX see the results of the two operations .
That is no proof, could be undefined behavior
it could be undefined behavior but if it's the case then it should change from one platform to another it produces the result as I said in Clion, codeforces platform and these other online IDEs
https://www.ideone.com/A37CME
https://onlinegdb.com/Sy1f-DfNz
http://cpp.sh/5frra
http://tpcg.io/bnedib
you can check it
First of all, it depends on the compiler, not the IDE. Then also it might change on a different platform, but it doesn't have to.
edit: I also found this, which says it's undefined behavior: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/526070/handling-overflow-when-casting-doubles-to-integers-in-c
if it's the same on different platforms , then how could it be undefined ? also is all these IDEs use the same compiler ?
yes it's indeed undefined in the older versions you can try it in c++98 or c++11 it won't be like that
undefined means that it's not specified in the C++ standard what to do for that scenario. Maybe all compilers implement the same solution, maybe some do it differently from others.
The standard specifications mention it is indeed undefined behavior (read here). In practice, modern compilers do indeed cast large float numbers to the maximal value acceptable, when cast to an integral type.
I think on F, that ans[0] = ans[1] = 0..
Thanks for the contest, it was fun!
Thank you, tutorial was updated, changes will come into force soon.
I used a greedy solution for question C .First I found out the bottle which has least value of cost per litre .Then I used a formula to give maximum possible number of bottles of this category(i.e. L/(volume of bottle of the category). Then i brute forced my solution ( i bought the best possible bottle at the moment by using a formula and then subtracted the volume from L, then repeat and repeat till L becomes <= 0 ). However, my solution failed on test case 14 of system testing. Here is my solution link My solution Any help would be appreciated. Thanks :)
It fails for the case:
30 842765745 2 2 2 4 6 8 12 12 18 28 52 67 92 114 191 212 244 459 738 1078 1338 1716 1860 1863 2990 4502 8575 11353 12563 23326
Its the 14th test case.
Implying your greedy is wrong! :v
I used quite similar greedy approach for problem C with one little modification and I got AC. Maybe someone will find it interesting. Firstly, let's sort the bottles by the cost per litre. Let's start from the cheapest of them going to the most expensive. Lets denote the size of the bottle i as V[i]. We have two different cases:
This solution seems nice to me. Here the it is 34026125 . Feel free to ask questions if something is not clear for you.
Nice solution! Can you explain how you got the intuition to sort by cost per unit volume?
Sure. I just thought about the greedy solution and then it was obviously, because the main idea in greedy is to buy the cheapest bottle.
Great set of problems.I liked the 3rd one most.Credits goes to @tourist, my man. Thumbs up for all the problem setters too.
Is there different kind of solution for problem C?
Here, 34034532 .
Same logic but a bit different implementation. :)
The solution I wrote only passes through the bits of L once, going from least-significant to most-significant. 34027236
If, at any time, buying bottle i would be better than the entirety of the sum we've already calculated, then replace the sum with the cost for bottle i.
E problem uses the same concept as F Problem of this contest.
I think E is suitable for smart or patient person. I quit immediately after reading it.
Misread problem D. How to solve the problem optimally when k >= a pj instead of k ≤ apj in problem D?
I think that the beauty of problem D comes when you think of it geometrically. Imagine that you have a point in the plane with coordinates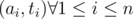 .
.
Then, for a fixed k, they are asking you a question about the points in a semiplane that lies to the right of the vertical line x = k, including the line (this is in the original statement with k ≥ apj, it lies to the left of that line if we choose k ≤ apj).
With this in mind, I think that both problems look more like a "Sweep Line" kind of task, doesn't it? (this is how I approached problem D during the contest, and why I believe that solution 2 in the editorial is more natural, although this last part is clearly subjective)
"it lies to the left of that line if we choose ....", not exactly. When we count problems in score such that k >= apj, we can choose problems on either side of the line. The points for which k >= apj are added to the score, however, we can choose points on other side of the line which don't satisfy this condition which will increase value of k (not increasing the score though), however this also moves the line and we can add new points with lesser ti such that k >= apz increases and we can replace few points.
Basically, when k >= apk, the final points/score will not always be equal to the number of problems we choose.
I misread it too and used the following idea. Let's sort our arrays in non-descending order of ai. Run a binary search on the value of x result points, and then say that the total amount of solved problems should be at least ai. Then for any j < = i j-th element can give us a point if we will take it and we will suppose now that all the elements right to the i-th will not give us a point(if they actually will we'll consider it later). So we should take x elements from the i - th prefix with minimum total time, and then we should take ai - x elements from all the array with minimum total time(except the taken ones). It also can be noticed(but it is not neccesary) that this check procedure for a given x is to find out whether there exists such i that the sum of minimum x elements from the i-th prefix plus sum of minimum ai - x elements from the i + 1-th suffix is no more than T. It can be implemented with two segment trees(for prefix and suffix elements) (where trees are build on the array sorted by the time now and making a transition from i to i + 1 we do some changes, and find the sum of some first values).
My rating is now fibonacci sequence (2358) :)
that rating was 2 years ago, what about now??
Can someone find out why this code for D.Too Easy Problems (based on binary search) get runtime error? http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/913/submission/34026112 Thanks in advance.
http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/913/submission/34035369
In your cmp function change <= to <
How can it cause runtime error? Is it about implementation of std::sort? Thank you for finding error :D
The reason is cmp(a, b) should return true only when a is strictly less than b (a < b). It should return false when elements are equal (a == b). If you use <= then for case a == b it will return true for both cmp(a, b) and cmp(b, a). For complier it means a < b and b < a at the same time so you will probably end up in indefinite loop.
Some links: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/concept/Compare and http://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/54610 (item 3)
Thank You [user:tourist]for nice and pretty problem. Now I am a Blue Coder :'(. I am Very Happy For That. :)
ууу матан, дайте задачки которые возможно решить 10-ти классникам :(
Its my first time seeing an Integral being applied in competitive programming (in problem H)! :3
There is this very interesting problem that uses integrals (now that I read H from this contest, the problems are somewhat similar).
EDIT: ok, maybe not that similar since in the problem I pointed out you could calculate the integral with general algorithms such as Riemann integration or Simpson's rule, whereas here you have to mathematically compute the integral since you need an exact answer.
http://main.edu.pl/en/archive/oi/11/zga
This one has integrals and it's also about gambling (a nice bonus of the problem!).
Solution to C using Binary Search: http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/913/submission/34035650
Can you explain your approach? Thanks!
Maintain a vector for the lemonade types and sort it according to the cost per liter(c[i]/(2^(i-1)). This sorts the lemonades according to the most optimal types of lemonade (cheapest lemonade) by normalizing the quantity to 1 liter. Thus we can greedily say that, if we buy lemonades in this sorted order, we can obtain maximum liters of lemonade from a given amount of money.
Therefore, now we can use binary search to fix the amount of money we have, and then see if it is possible to obtain atleast L liters of lemonade by traversing in this sorted order and taking as many no. of lemonades of each type as possible.
Hence, amount of money used can be easily minimized.
3 7 5 11 18
what about this case? are you sure your code passes this case? UPD: Got it. I was wrong.
ok. I checked this case against LGM's code. Your code gives similar to them. But how its 33? shouldn't it be 34?
Buy 3 one liter bottles, cost=3*5=15 Buy 1 four liter bottle, cost=18
Net cost=15+18=33 to buy 7 liters of lemonade
Nice approach, I had the same idea but was not sure how to use binary search.
In problem C purpose of doing the following is? L -= need << i;
you are taking "need" number of bottles of 2^i size. "need << i" is basically "need * (2^i)"
got it,thanks
Пытался решить задачу E (Логическое выражение) поиском в ширину (или даже больше на Левита похоже):
1) создаем массив string-ов
formulasдлинны 256, где по "вектору значений" функции будем хранить функцию ответ на задачу2) существует всего 3 функции длинны 1 (
"x", "y", "z"), добавляем их в очередь3) пока очередь не пуста:
* вычисляем
val— значение текущей функции на всех возможных аргументах* если для
formulas[val]еще не вычислен или мы нашли более удачную функцию, то обновляем значение в массиве и пытаемся "расширить"/"дописать" данную функцию, для нахожения остальных формулформулу
fя расширял по следующим правилам:!f,f&x,f&y,f&z,f|x,f|y,f|z,!(f),f&!x,f&!y,f&!z,f|!x,f|!y,f|!z,(f)&x,(f)&y,(f)&z,(f)|x,(f)|y,(f)|z,(f)&!x,(f)&!y,(f)&!z,(f)|!x,(f)|!y,(f)|!zтаким образом мне удалось найти только 218 функций.
видит кто-нибудь ошибку? или просто я побрел не в ту степь?:)
Надо расширять до f & g и f | g для всех пар функций f и g, найденных к текущему моменту — тогда решение заработает.
спасибо, я так тоже сделал, тогда находятся все функции, но не обязательно оптимальные по длинне / лексикографическому порядку
Can anyone tell why my code for C is failing for last sample input. The logic is similar to editorial. Link to my solution : My Solution
See for example the following test case:
5 7
1 2 3 4 9
The correct output is 4 (take one bottle of 8 liters) but your answer gives 6.
Hope this helps you!
Thanks a lot! Understood my mistake
for problem G,the tutorial says "In this problem n ≤ 11. m = 6 is enough for such n",why 6 is enough?
m = 6 is enough because if n ≤ 11 then 10m ≥ 2·2n + m.
Let x = a·10m. If x is not divisible by 2n + m, we add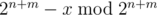 to x. After that if x is divisible by 5 we add 2n + m to x.
to x. After that if x is divisible by 5 we add 2n + m to x.
After such transformations x is divisible by 2n + m, x is not divisible by 5 and x ≤ a·10m + 2n + m - 1 + 2n + m. We know that 10m ≥ 2·2n + m. Therefore b = x - a·10m < 10m. That's exactly what we want.
thank you! I didn't understand clearly why "10^m ≥ 2·2^(n + m)" <=> "there exists k satisfying equation (1) and (2)" earlier, and after read your tutorial more carefully, I got that "Consider equation . Every number in the equation is divisible by 2^(n + m), lets divide all the numbers by this. The result is — equation (3) where . Use the following lemma: Lemma For every positive integer t number 2 is primitive root modulo 5^t." shows why "10^m ≥ 2·2^(n + m)"<=>"there exists k satisfying equation (1) and (2)", and we just need to find any k under these assumes. In this way the range of an available m can be determined, very nice problem!
when 10^m>=2^(n+m+1), then b can choose from [0,10^m-1], since 2^(n+m)-1<2^(n+m+1)-1<=10^m-1, so the values of b can cover [0,2^(n+m)-1], thus there exists some b satisfying ai*10^m+b=0(mod 2^(n+m)) and let x=ai*10^m+b, so x/2^(n+m)=2^(k-n-m)(mod 5^(n+m)), since 2 is a primitive root of 5^(n+m), so there exists t in range[0,4*5^(n+m-1)) satisfying 2^t=x/2^(n+m)(mod 5^(n+m)), then let k=n+m+t>=n+m, this k is the answer to the problem
a way to prove 2 is primitive root of 5^k (k>=1) using induction: assuming (I) 2 is primitive root of 5^k, and (II) 2^phi(5^k)≠1(mod 5^(k+1)) first, about (II) 2^phi(5^(k+1))-1=2^5phi(5^k)-1= (2^phi(5^k)-1)*(2^4phi(5^k)+2^3phi(5^k)+2^2phi(5^k)+2^phi(5^k)+1) since 2^phi(5^k)=1(mod5^k) (using euler's theorem) and 2^phi(5^k)≠1(mod5^(k+1)) (by assuming),therefore gcd(5^(k+2),2^phi(5^k)-1)=5^k if 5^(k+2)|2^phi(5^(k+1))-1 then there must be 5^2|2^4phi(5^k)+2^3phi(5^k)+2^2phi(5^k)+2^phi(5^k)+1 but 2^phi(5^2)=1(mod 25), thus 2^(sphi(5^k))=(2^phi(5^2))^(s*5^(k-2))=1(mod 25) so 2^4phi(5^k)+2^3phi(5^k)+2^2phi(5^k)+2^phi(5^k)+1=5(mod25) so 2^phi(5^(k+1))≠1(mod 5^(k+2))
then about (I) for t in range [0,phi(5^(k+1))), 2^t=1(mod5^(k+1))=>2^t=1(mod5^k)=>phi(5^k)|t let t=phi(5^k)*s, since 0<=t=phi(5^k)*s<phi(5^(k+1)) so 0<=s<5, consider 2^t-1=(2^phi(5^k)-1)(2^(s-1)phi(5^k)+2^(s-2)phi(5^k)+....+1) so 5^(k+1)|2^t-1 <=> 5|2^(s-1)phi(5^k)+2^(s-2)phi(5^k)+....+1 since 2^phi(5^k)=(2^4)^(5^(k-1))=1(mod5) so 2^sphi(5^k)=(2^phi(5^k))^s=1(mod5) so 2^(s-1)phi(5^k)+2^(s-2)phi(5^k)+....+1=s(mod5) thus 5|s and 0<=s<5 => s=0 thus for t in range [0,phi(5^(k+1))),2^t=1(mod5^(k+1))=>t=0, implying that 2 is primitive root of 5^(k+1)
somewhat tedious
I made two mistakes in Problem C during the contest. 34026884 First doesn't deal with a empty tail at last. Second fail to score the status and made a lot of unnecessary calculation which made TLE. My solution is too complex in all. Any suggestion in shorten the code?34038638
can't we slv B. Christmas Spruce with c ?
Did you mean C language? In this task yes. But usually you can get 105 vertexes with [0;n - 1] edges (of course you can't create array [105][105]). That's why it is recommended to use C++ for sport programming :)
For problem C fourth example, why i get 44981600797903355?
I was getting that too. You must have some index of array which is getting negative.
No, my solution is wrong.. Thanks for commented
Somebody please explain for Problem E,How the number of functions are 256 and number of states are 3256?
i use dfs to solve the problem C 34018956
Можно пояснить про E?
Что подразумевается в данном случае под нетерминалом и почему количество возможных функций умножается на всего лишь на 3?
Нетерминалы — переменные из грамматики, в данном случае это
E,T,F.Состояние — пара (нетерминал; функция). Таких пар 3·223.
for problem 913D- Too Easy Problems
"The first observation is that if we solve a problem which doesn't bring us any points, we could as well ignore it and that won't make our result worse. Therefore, there exists an answer in which all problems bring us points. Let's consider only such answers from now on."
I don't think this is true,
Test Case
We solve 1,2,3 to make 1 points, Problems 1,2 don't bring us points but help increase the number of problems solved thus helping us solve problem 3 to earn 1 point.
Please let me know if I am stupid and have got it all wrong
What he meant is, there exists an answer where all problems ATTEMPTED brings us points.
So, in your example, we could have just attempted the 3rd problem and it would have brought us 1 point (and 1 answer attempted only)
i get it, my bad. thanks for pointing out
please ignore the previous comment
In Problem D what if the score was only added when you have solved a[i] problems . Can anybody suggest a solution for that ?
can we solve E using Karnaugh maps??
In problem F, Strongly Connected Tournaments, can someone tell me how the law of total probability applies in each of the cases?
Why my solution failed on the 18th test case. On my machine, it's giving the right output. Why so?
34011797
I'm guessing it's floating-point precision errors. Probably the calculation of log_2(m) is not exact when you do log_10(m)/log_10(2) as floating-point numbers, so the comparison against n may be wrong.
But in this test case log_2(m) is giving 25 . Hence if the condition would fail in this case and the output would be m%pow(2,n) would give 0 . Where is the mistake here ?
25 33554432
yes, but you're storing all of these as floating-point numbers. Thus, the actual representation may not be exact, and doing equality comparisons or comparisons when the values should be equal to each other may be wrong. This might be why it failed on that test case.
It may also be some weird C++ memory thing. I also discovered that if you change both variables to float (instead of one double and one float), then it passes all testcases. See the modified submission: 34077845
Alright,thanx that's ohkay . But what if I typecast log_2(m) to long long and then compare m and log_2(m)
In that case also its not working . why so ?
probably because long long is an integer type. log_2(m) might not be an integer.
Has anyone solved E using Sum of Products(SOP) form, then minimizing the terms using K maps or algebraic minimization and then finally combining terms to get lexicographically smallest function ?
I thought that it's the solution and pass the problem ASAP. However I think it can really work with some effort.
i didn't understand problem E. can anyone please explain me that problem a little bit.
can someone explain me please what does he consider by states in the editorial of E and what does nonterminals from the right part of the rule mean ? Help would be appreciated !
I have a question about the problem F.
When we compute cp(s, i), if we think that we add a new player with the largest index, then the following equation holds: cp(s, i) = cp(s - 1, i) × (1 - p)i + cp(s - 1, i - 1) × ps - i.
But I thought that I add a new player with the smallest index. The equation below is what I made.
cp(s, i) = cp(s - 1, i) × pi + cp(s - 1, i - 1) × (1 - p)s - i
I cannot find why I was wrong... I've spent almost two days in order to solve this problem...
Could you tell me what I am doing wrong?
I explain about my equation.
I'm going to add a new player whose index is the smallest. There have already been s - 1 players. After adding a new player, the number of players should be s.
The first term, cp(s - 1, i) × pi, describe the case when a new player is not in the set of i players who lose to the others. The 'new added player' must win all the i players who are in the set. Thus, the probability is pi.
The second term, cp(s - 1, i - 1) × (1 - p)s - i, describes the case when a new player is in the set. The 'new added player' must lose to all the s - i players who are not in the set. Thus, the probability is (1 - p)s - i.
Would you tell me what is wrong?? Why should I add a largest-index-player like the official solution?
This way of computation of cp(s, i) is correct too. Maybe you have a mistake in other part of solution.
Thank you very much! I really appreciate your help.
I have a binary search solution for C, I did binary search on cost available and checked if maximum volume that can be bought is greater than volume required and in this way calculated minimum price. I passed the pretests but got wrong on 14 test case, it was due to overflow. After correcting overflow I got it accepted. Here is my submission.
In Solution of 913C ,in the following line
// ans = min(ans, sum + (L > 0) * c[i]); //
what is significance of (L>0) ????
Remember that after you alter the domain as a[i] = min(2*a[i-1], a[i]), it makes sense to buy ith bottle as opposed to two i-1 bottles. So if L > 0, it means there is volume left, and it makes no sense to retain the bottles you picked previously, so get that extra ith bottle. As explained in editorial, if you set left most bit to 1, all the right side bits can be set to zero as the answer will still be maximum.
No , I'm talking about code of solution.
L = 0, (L > 0) equals to 0 (false)
L = 1, (L > 0) equals to 1 (true)
Can someone explain E clearly? I fail to understand what a state represents!
"It can be shown that the answer can be represented as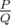 , where P and Q are coprime integers. Print the value of P·Q - 1 modulo 998244353."
, where P and Q are coprime integers. Print the value of P·Q - 1 modulo 998244353."
P·Q - 1 ==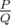 , so it is a fractional number, isn't it?
, so it is a fractional number, isn't it?
https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/cryptography/modarithmetic/a/modular-inverses
Hey can someone tell me where I am wrong...this code is giving wrong answer on 17th test case... Problem B
http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/913/submission/34023515
Wow, problem G was really great! I also really liked problem F. Good work YakutovDmitriy :)
The solution of these problems was very clear! Thanks for the analysis and solution.
Good problems,I like it!
I tried modular exponentiation, but failed on test case 3. What do I need to do?
include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long power(long long A, long long B, long long mod) { if (B == 0) return 1;
long long res = power(A, B / 2, mod); res = (res * res) % mod; if (B % 2) res = (res * A) % mod; return res;}
int main() { long long n, m; cin >> n >> m; long long result = power(n, 2, m); long long ree = m % result; cout << ree << endl; return 0; }