The round has finished. I hope you liked it!
Credits to the round authors and developers:
1110A - Parity. Authored by _h_ and simonlindholm.
1110B - Tape. Authored by _h_ and simonlindholm, development: cdkrot
1110C - Meaningless Operations. Authored by GreenGrape
1110D - Jongmah. Authored by _h_ and simonlindholm, development: KAN and MikeMirzayanov
1110E - Magic Stones. Authored by _h_ and simonlindholm, developed by GreenGrape
1110F - Nearest Leaf. Authored by grphil, developed by vintage_Vlad_Makeev
1110G - Tree-Tac-Toe . Authored by cdkrot and KAN
1110H - Modest Substrings. Authored by _h_ and simonlindholm, development: budalnik
And now, the editorial:
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...
Tutorial is loading...










In C,
If we precalculate answers for all a=2^x−1 up to m=2^23−1. Shouldn't it be 2^25-1?Corrected thanks!
We indeed increased constraints slightly before the contest.
Can you point me to where I am wrong in the third question? My approach was somewhat like this I took the intervals of the numbers ie A[i]-A[i-1] and stored them in one vector and sorted them in decreasing order Now I can make 'K' tape which means I can use K-1 use non attached tapes right... so I took the sum of all the intervals and deleted the first k-1 larger intervals from the sum that is sum-v[0]-v[1]-..v[k-2].. and then printed out (sum+k) as the final answer I got stuck in the test case number 9 ... Thanks in advance for your help.
Probably one of the most well written editorial i have ever seen!
Can someone please explain the solution of B in more detail?
Suppose, We have a stick with 100 cm length and 8 broken points,
.........10.12.... .....30....35..... .......80.....86......93.........100...
Since, there are 8 broken points and each point takes 1cm, at the very least we need 8cm tape to fix them. But with the constraint of number of tapes, we will have to cover a segment instead of a point. In the process, we will end up covering some unbroken points. So, total covered points will be the broken points + the points which fall under those segments that we picked to cover due to the constraint.
Consider the following cases -
Case 1: k = 8
We have 8 tapes to use. So, there is no point wasting tape on unbroken points. Just cut 8 tapes of 1 cm, and fix the broken points. So, we are only using 8 cm of tape, no tape wasted. Cool!
Case 2: k = 7
We have 7 tapes to use. Now, we are 1 piece short. So, we will fix a segment with one tape (instead of just a point) and for rest of the broken points we can just put 1cm pieces.
So, how do we choose that special segment? The goal is to waste as little as possible tape. Looking at the pipe above, we would like to cover 10.12, just wasting a 1cm tape. This will make us to cover point 11 which is not broken. But there is no better way.
So, how much tape we are using now? 8 broken, 1cm points + 1 extra 1cm point = 9cm
Case 3: k = 6
We have 6 tapes to use. Using the same approach on Case 2, we have to pick another segment. 30....35 is our next best option, because we are justing wasting 4cm tape in the middle.
Thus 8cm legit broken points + 1cm in the middle of 10.12 and 4cm in the middle of 30....35 = 13 cm
So, we will be needing to cover up the short amount of tape, and we will choose the segments which come with little waste of tape. To find those segments, we need to list all b[i+1] — b[i] — 1, meaning the lengths of non-broken segments. Now, we will just cover the smallest (n-k) of the segments we need to.
Thanks!
Thanks for fast tutorials
can someone explain tape (2 question) in better way
hey I will explain it with help of one example; let n=10, n=35, k=5; b[i]={1 2 5 6 9 11 13 15 23 27} broken segments; 1_2__5_6___9__11__13__15________23___27_ (where you have to repair I have put that integer no.)
if you have value of k more than n (k>n), then you can easily cut the 10 segment of 1cm so it will very less tap require(only total 10cm tap required=10cm(1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm+1cm). But here the value of k is 5 so you have to cut 5 segment such that all broken part should cover.
1_2__5_6___9__11__13__15________23___27_ (where you have to repair I have put that integer no.)
now if you cut 1cm of 10 segment tap it is less tap required but you can cut only 5 tap segment because k value is 5.
so you will cut 5 segment such that segment cover max length with small tap. now a[i]=b[i+1]-b[i] So a[i]={1,3,1,3,2,2,2,8,4} so by sorting it a[i]={1,1,2,2,2,3,3,4,8} So you will repair first all that segment which are very near means 1 and 2, 5 and 6, and so on.. you can cut the tap at most five times(k value), so your target is with this five segment you have to repair the stick.
Why is that implied in this case?
When a=2^x-1,it's binary will have all bits as 1.So, a&b equals b and (a xor b) equals a-b.
Thanks for quick response!
Why is the largest proper divisor the answer? Does it relate to the Extended Euclidean algorithm?
Notice that when b is divisor of a,a-b will also be the divisor of a. So,maximum possible gcd(a-b,b)=largest divisor of a.
I think you meant that, when b is a divisor of a, a - b will be divisible by b, didn't you?
Oh...Yes
gcd(a-b, b) eqaul to b when b is factor of a.
Can you point me to where I am wrong in the third question? My approach was somewhat like this I took the intervals of the numbers ie A[i]-A[i-1] and stored them in one vector and sorted them in decreasing order Now I can make 'K' tape which means I can use K-1 use non attached tapes right... so I took the sum of all the intervals and deleted the first k-1 larger intervals from the sum that is sum-v[0]-v[1]-..v[k-2].. and then printed out (sum+k) as the final answer I got stuck in the test case number 9 ... Thanks in advance for your help.
I expected more than on G. Since it is just working with cases. The idea is obvious.
Well, yes, but there are several cute ideas along the way (that the degrees are small and and the idea about reducing the problem to uncolored vertices only, which is not mandatory to get AC, but helps greatly)
can you explain part B
But there is an editorial written already...
Ask some concrete question at least.
What I want to know is, why have people stored the differences as b[i] — b[i — 1] — 1 and added n to the answer?
Looks fine to me, basically you need to spend tape to cover the broken segments themselves ( + n in the end) and then you only care about which gapes between segments are "collapsed" into single tape part and which are not.
Got it, thank you!
Can you point me to where I am wrong in the third question? My approach was somewhat like this I took the intervals of the numbers ie A[i]-A[i-1] and stored them in one vector and sorted them in decreasing order Now I can make 'K' tape which means I can use K-1 use non attached tapes right... so I took the sum of all the intervals and deleted the first k-1 larger intervals from the sum that is sum-v[0]-v[1]-..v[k-2].. and then printed out (sum+k) as the final answer I got stuck in the test case number 9 ... Thanks in advance for your help.
Anybody solved D with greedy?
In D, Can you please explain the statement — So we can assume that there are at most 2 triples of type [x,x+1,x+2] for each x.
It means that given some x, it isn't necessary to try choosing the triplet [x, x+1, x+2] more than 2 times. Because for k > 2 (assume km = k mod 3), k[x, x+1, x+2] is equivalent to km[x, x+1, x+2] +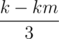 [x, x, x] +
[x, x, x] + 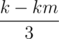 [x+1, x+1, x+1] +
[x+1, x+1, x+1] + 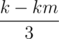 [x+2, x+2, x+2].
[x+2, x+2, x+2].
what do you mean by it doesn't make sense ? what will happen if we choose triplet (say) 3 times ?
And how dp state is formulated ? can you describe a little bit.
As k[x, x+1, x+2] is equivalent to km[x, x+1, x+2] + (k-km)[x] + (k-km)[x+1] + (k-km)[x+2], you can use this observation to apply simple dp that tries to take a triplet [x, x+1, x+2] at most only 2 times, and gives you the same optimal answer.
so , in the optimal answer there will be no triplet like [x,x,x] ?
do we have to form triplets only using [x,x+1,x+2] . only it will give optimal answer ?
In the dp when you consider element x, you make 3 trials. In the jth trial (j ranges from 0 to 2), you try to take the triplet [x, x+1, x+2] j times (if minimum(count(x), count(x+1), count(x+2)) >= j), and you add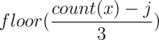 to the jth trial's result. So basically, what is left from x in the jth trial is just consumed in the form of triplets [x, x, x].
to the jth trial's result. So basically, what is left from x in the jth trial is just consumed in the form of triplets [x, x, x].
can you explain by writitng the recurrence relation for dp ?
One possible way:
Let dp[i][j][k] be the maximum count of triplets that can be formed if you start at value i, j occurrences of value i and k occurrences of value i + 1 are consumed in the form of triplets [x, x + 1, x + 2] where x < i. And let co[i] be the initial count of value i occurrences.
For 0 ≤ l ≤ 2, if min(co[i] - j - l, co[i + 1] - k - l, co[i + 2] - l) ≥ 0,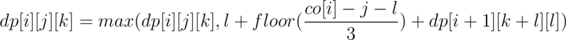 (where dp[i][j][k] is initially 0). The answer is dp[1][0][0] (Loop order: i = m → i = 1).
(where dp[i][j][k] is initially 0). The answer is dp[1][0][0] (Loop order: i = m → i = 1).
Why are you considering l upto 2 why not till min >=0 ?
Read my first two replies to the top level comment.
thanks alot
Sir, why are you adding floor((count(x) — j)/3) to the jth trial?
Because you consumed j occurrences of x in form of triplets [x, x + 1, x + 2]. So you want to consume what is left from x in form of triplets [x, x, x] (and if 2 or 1 occurrences of x are left at the end, you will not use them). This is equivalent to taking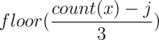 .
.
Got it now, thanks !!
Fast editorial.Great!
Hi everybody,
In case anybody needs practice with B, AtCoder Beginner Contest 117 had a very similar problem here.
Here is my editorial for Problem C. I believe it is easier to understand than the editorial provided here. Let me know if you have any doubts. :)
Here is my editorial for E.
Thanks a lot!! nice explanation
In C, if a=2^x . Then as per "Denote the highest bit of a as x (that is largest number x, such that 2^x≤a) and consider b=(2^x−1)⊕a. It's easy to see that if a≠2^x−1 then 0<b<a holds." b=2^(x+1)-1. which does not hold in between 0 and a.
It's probably a mistake. I think b should be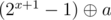 .
.
Thanks a lot !
I was wondering for a long time until I found that it's a mistake
Has anyone solved "D" using greedy approach? If yes, can you please share!
how to dp in AC automaton? how to calculate the answer of all the current suffixes? Could you explain in details. thanks cdkrot
In C, we denote x as 2^x <= a, but then the explanation states the following: "consider the case when a=(2^x)-1". Could someone explain what they exactly mean here?
It should read "consider the case when a=2^(x+1)-1". I was also confused by that. Basically, a is a string of 1s in binary.
can someone tall the c++ codes for 2nd and 3rd question, maybe with comments and steps will be more helpful
I think in C editorial, meaning of x should be the smallest number such that 2x > a.
Thanks for the editorial. I didn't realize the editorial was already out, cause I didn't see the "Recent actions" so much. Adding a link to the original announcement blog post ( http://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/65059 ) would be helpful :)
In fact, we can use a simple way to solve the problem C.
Although this way is not very good.
Can anyone explain me the intuition behind the process in problem E ? Its hard to come up with such an idea
This comment and read the editorial to the problem: http://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/65059?#comment-490669
It's not obvious to me how to come up with such idea, it just seems like its a tricky known technique :S
Please correct me if I'm wrong but it seems that in C the given editorial solution leads to wrong answer. For eg. if a=11 then given solution would give b=12. Instead it should have been b=4 (which we get by complimenting binary rep of a=11, considering significant bits).
See this: https://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/65079?#comment-490920
Can anyone please explain the solution to D in more detail? (Like the exact dp equation and its initial values) My mind got a bit mixed up...
I think this blog will help. https://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/65092
Could someone explain how to come up with such a dp state in problem D?I'm curious because I can't figure it out.
Can someone elaborate more on E? I can't quite understand why this equations proves that you need to check array difference.
Hello!You can try some more complicate examples to find that it's obvious that the array difference with the first and the last number determines the result.By the way, there is a conclusion:if you can exchange any two neighbor elements in a array, you can obtain any permutation of this array.I help this helps:)
Yes, thank you. In meantime I figured it out.
please someone elaborate more on F
I was trying to solve problem 1110F - Nearest Leaf offline, using centroid decomposition but is giving me TLE 49838550, any ideas? I know it might sound as an overkill but still it's complexity is something about O(NlgNlgN + QLgNlgN). thanks
In Problem B, we will calculate the differences between every two adjacent broken points and store them in a sort array of size n-1. Now lets assume that we need to cover all the broken points with one piece of tape. For this the answer will be [difference of first and last element of the given array + 1] . Now we will optimize the answer as we have the chance to us at most k pieces of tape. We will subtract [x-1] form the answer for each of the last [k-1] elements of sorted array (where x is an element of the sorted array).
Code Snippet
In question 1110A-Parity , can someone explain what is the error in my code :
It is giving wrong answer in one of the test cases.
For the sake of precision, don't use pow() with integers, ever.
Problem D.
Why does my solution in java fails in memory if it uses just MAX*5*3 of integers? https://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/1110/submission/51139125
Because recursive calls themself also consumes O(N) memory in total. Each call there are multiple ints used, such as the parameter passed in, local variable, etc.
GreenGrape For 1110C — Meaningless Operations, Can you explain Why you take
b=(a xor (2^x-1))it looks bias,can you explain it more?We try and make (a xor b) = 2^x-1 if possible{when a!= 2^x-1},since we notice that if (a xor b)=2^x-1, then (a & b) is 0, and gcd(x,0) = x Now, since (a xor b) = 2^x-1, b = (a xor 2^x-1)
hey guys!!! can anyone pls tell why binary search doesnt work for the Problem B (Tape)
My Code for the same
Did you get the answer?
My code also failed on test case 7 while using binary search:
303771266