Hello Codeforces community.
Tl;dr: The script is specifically for *Unix and can be used to stress test `C++` solutions. It can be easily modified to work with python or java. To use it in windows you can download Ubuntu terminal which is officially available on Microsoft Store and then use it or you can modify the script to work in cmd by changing the .out files to .exe and a bit of syntax for cmd.
Note: If you don't want to read this lengthy blog, just go to this repo and follow the instructions of readme.
First let me tell you what stress testing is if you don't know, Stress testing is technique using which we can run our solution (which we think might fail/is failing) on a number of random test cases and match it's output with the output of a solution which is a brute force solution or accepted solution of someone else.
If you don't know why and when to use stress testing you can use this detailed article on Stress Testing by ADJA.
I want to share my script for stress testing your solution.
Requirements:
1) A solution which we want to test.
2) A brute force solution which gives correct solution.
3) A generator for generating test cases according to the problem.
About script:
code#!/bin/bash
# To color the output text in different colours.
green=$(tput setaf 71);
red=$(tput setaf 1);
blue=$(tput setaf 32);
orange=$(tput setaf 178);
bold=$(tput bold);
reset=$(tput sgr0);
CPP_VERSION="c++17"
COMPILE_FLAGS=""
TC_GENERATOR_FILE="tc_generator.cpp"
MAX_TESTS="10"
BRUTE_FILE=""
MAIN_FILE=""
############################################################
# USAGE
usage(){
echo "
USAGE:
$$$(basename "$$${0}") -b <brute-sol> -m <main-sol> [ -t <no.-of-testcases> ]
Options:
-b <brute-file> Specify the name of cpp file having brute force solution. [required]
-m <main-file> Specify the name of cpp file having main solution. [required]
-t <integer> No. of test cases to generate and stress test on. (optional, default 10)
"
}
# Checks if the main, brute and generator files exists or not.
function check_files_exists() {
declare -a cpp_files=("$1" "$2" "$3")
for file in "${cpp_files[@]}"; do
# echo "${file}"
if ! [[ -f "$file" ]]; then
echo "File $$${orange}$$${file}$$${reset} does not exist in dir $$$(pwd), exiting..."
exit 1
fi
done
}
# Compiles a given cpp file and stores the executable in variable `executable_fname`
function compile() {
local cpp_file="$1"
local executable_fname="$2"
local start_time="$(date +%s)"
g++ -std="$$${CPP_VERSION}" "$$${cpp_file}" -o "$$${executable_fname}" "$$${COMPILE_FLAGS}" || { echo "$$${bold}$$${red}Error when compiling: $$${reset}$$${orange}$$${cpp_file}$$${reset}"; exit 1; }
local end_time="$(date +%s)"
echo "$$${green}Successfully compiled $$${cpp_file}$$${reset} in $$${orange}$$$((end_time - start_time))s$$${reset}."
}
function cleanup() {
rm -f input1.txt generator original brute original_output.txt brute_output.txt
}
function tips() {
echo ""
echo "$$${blue}You might want to use $$${green}https://www.diffchecker.com/diff${reset} to better visualize the difference in output :)${reset}"
}
function stress_test() {
local diff_found=0
echo "" && echo "Starting stress testing on $$${orange}$$${MAX_TESTS}${reset} randomly generated test cases:" && echo ""
for ((i=0; i<$MAX_TESTS; i++)); do
# Generate test_case and save it in input1.txt
./generator > input1.txt
# run original solution, take input from above generated test case i.e. from input1.txt
# and save it in original_output.txt
./original < input1.txt > original_output.txt #|| {echo failed; exit 1;}
# run brute force solution, take input from above generated test case i.e. from input1.txt
# and save it in brute_output.txt
./brute < input1.txt > brute_output.txt
# check if files original_output and brute_output
# differs(we are ignoring spaces and then comparing files)
if diff -F --label --side-by-side --ignore-space-change original_output.txt brute_output.txt > /dev/null; then
echo "<p>Unable to parse markup [type=CF_MATHJAX]</p>{bold}$$${green}passed$$${reset}"
else
echo "<p>Unable to parse markup [type=CF_MATHJAX]</p>{bold}$$${red}failed$$${reset}"
diff_found=1
break
fi
done
if [[ $diff_found -eq 1 ]]
then
echo "$$${blue}Input: $$${reset}"
cat input1.txt
echo ""
echo "$$${blue}Output(Main sol): $$${reset}"
cat original_output.txt
echo ""; echo ""
echo "$$${blue}Expected(Brute sol): $$${reset}"
cat brute_output.txt
echo ""
tips
fi
}
function main() {
# Parse args
while [[ $# -gt 0 ]]; do
case $1 in
-b)
BRUTE_FILE="$2"
shift # past argument
shift # past value
;;
-m)
MAIN_FILE="$2"
shift
shift
;;
-h)
usage
exit
;;
-t)
MAX_TESTS="$2"
re='^[0-9]+$'
if ! [[ $MAX_TESTS =~ $re ]] ; then
echo "error: argument -t must be a number e.g. -t 69 "; exit 1
fi
shift
shift
;;
-*|--*)
echo "Unknown option $1"
exit 1
;;
esac
done
check_files_exists "$$${BRUTE_FILE}" "$$${MAIN_FILE}" "${TC_GENERATOR_FILE}"
compile "${TC_GENERATOR_FILE}" "generator"
compile "${MAIN_FILE}" "original"
compile "${BRUTE_FILE}" "brute"
stress_test
}
main "$@"
Go through the code once, i have added comments and you will understand most of the part. To understand the script all we need is just basics of the language bash. So we have three .cpp files:
1) gen.cpp // our cpp solution for generating test cases
2) solution.cpp // our orignial solution
3) brute.cpp // our solution which uses brute force and guaranteed to give correct output
About test case generator:
For generating test cases you can either use "testlib.h" here (i personally don't use it because it takes 6-7 seconds on average to compile in my pc(idk there might be ways to reduce it) and also i need to remember the methods to generate things.) or write your own since most of the time you just need arrays, strings, trees or simple graphs or simple some integers.
I use the below code for generating test cases most of the times(file gen.cpp):
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define accuracy chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count()
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i = a; i <= n; ++i)
const int N = 1e6 + 4;
int32_t permutation[N];
mt19937 rng(accuracy);
int rand(int l, int r){
uniform_int_distribution<int> ludo(l, r); return ludo(rng);
}
const int inf = 1LL << 31;
using pii = pair<int,int>;
namespace generator {
string gen_string(int len = 0, bool upperCase = false, int l = 1, int r = 26) {
assert(len >= 0 && len <= 5e6);
string str(len, (upperCase ? 'A' : 'a'));
for (char &ch: str) {
ch += rand(l, r) - 1;
}
return str;
}
vector<int> gen_array(int len = 0, int minRange = 0, int maxRange = inf){
assert(len >= 0 and len <= 5e6);
vector<int> a(len);
for (int &x: a) x = rand(minRange, maxRange);
return a;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> gen_tree(int n = 0){
assert(n >= 0);
vector<pii> res(n ? n - 1 : 0);
// if you like to have bamboo like tree or star like tree uncomment below 8 lines
/*if (rng() % 5 == 0) { // bamboo like tree
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) res[i-1] = {i, i + 1};
return res;
}
if (rng() % 7 == 0) { // star tree
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) res[i-2] = {1, i};
return res;
}*/
iota(permutation, permutation + 1 + n, 0);
shuffle(permutation + 1, permutation + 1 + n, rng);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i){
int u = i, v = rand(1 , i-1);
u = permutation[u], v = permutation[v];
res[i-2] = minmax(u, v); // u < v, just for convenience while debugging
}
shuffle(res.begin() , res.end() , rng);
return res;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> simple_graph(int n = 0, int m = 0) {
assert(n > 0 && m >= n);
int max_edges = n * (n - 1) / 2;
assert(m <= max_edges);
vector<pii> res = gen_tree(n);
set<pii> edge(res.begin(), res.end());
for (int i = n; i <= m; ++i) {
while (true) {
int u = rand(1, n), v = rand(1, n);
if (u == v) continue;
auto it = edge.insert(minmax(u, v));
if (it.second) break;
}
}
res.assign(edge.begin(), edge.end());
return res;
}
}
using namespace generator;
template<typename T = int>
ostream& operator<< (ostream &other, const vector<T> &v) {
for (const T &x: v) other << x << ' ';
other << '\n';
return other;
}
ostream& operator<< (ostream &other, const vector<pair<int,int>> &v) {
for (const auto &x: v) other << x.first << ' ' << x.second << '\n';
return other;
}
// comment the just below line if test cases required
#define SINGLE_TEST
const int max_tests = 10;
// complete this function according to the requirements
void generate_test() {
int n = rand(1, 40);
cout << n << '\n';
cout << gen_array(n, 1, 20);
}
signed main() {
srand(accuracy);
int t = 1;
#ifndef SINGLE_TEST
t = rand(1, max_tests), cout << t << '\n';
#endif
while (t--) {
generate_test();
}
}
You can use above code and modify it according to your needs. Just go through the code once and everything is self explanatory(i have added some comments too). Usage of above gen.cpp code:
1) to generate an array calling:
gen_array(10, -5, 10);
it will return an array(vector more specifically) with length 10 and elements in the range [-5, 10].
2) to generate a tree calling:
gen_tree(10):
will return a tree with 10 nodes.
3) to generate a simple graph calling:
gen_simple_graph(10, 12);
will return a simple connected graph with 10 nodes and 12 edges.
You can add things as you need them or use testlib which is the best if you know how to use it.
Usage:
Download this repository manually or by using git clone on terminal.
- Copy your original solution which you expect might fail in the file
solution.cpp.
- Copy your brute force solution which is expected to give correct output in the file
brute.cpp.
- Change the
gen.cpp file so as to generate test cases according to the question.
Now open your terminal in the directory where file s.sh resides and run command:
$ bash s.sh
or
$ ./s.sh
If it shows permission denied then give it execute permission using:
$ sudo chmod +x s.sh.
In file s.sh you can change the value of variable max_tests as you wish on how many random test you want to run the solution.
Verdict: the verdict of running file s.sh on every test case is either Accepted if your solution's output matches the brute solution output or Wrong Answer and will show the input on which the solution failed, the output of your solution and expected output according to the brute force solution on terminal and the script will be terminated.
If you wish to terminate the script at any moment you wish use the command ctrl + c in terminal.
quick demo: Here the output of first 3 test cases matched with the brite and as soon as it didn't, it printed the test case, output, and expected output to the console and terminated. Now you can debug your original solution and check where it goes wrong.
(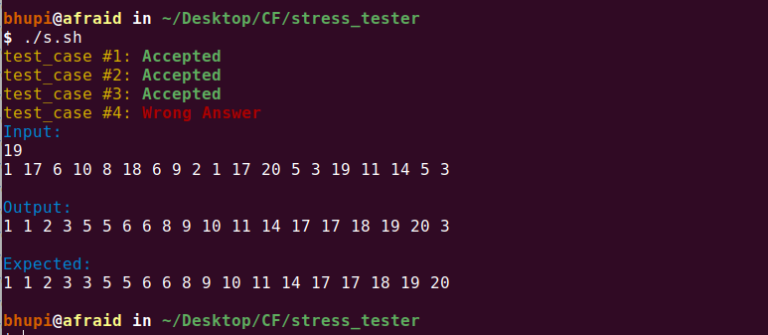 )
)
You can watch this video by Errichto to understand more about stress testing.
Any suggestions or corrections are welcomed.
Apologies for my poor English.
UPD1: Updated the script to take brute and main file via flags, no. of testcases as optional, added help/usage flag and updated readme for better readability & usage. Tested on Mac & Ubuntu, bash 5.x. Please refer updated README here for usage.
 )
) 










Suggestion — Maybe include the option to add a checker, because many problems have multiple possible solutions. Keep a default checker as a direct comparison of solutions, but allow the user to write his own.
Thanks for the suggestion. I will try writing one and update it.
If you want to test
cpp / c / java / python, you can checkout thisHow do I generate a binary string using the generator? please answer..
I think this should do the job:
or maybe like this:
sorry for a silly doubt but this wont work in cases when there are multiple possible solutions right
Yes, you are right. But for such case you can write custom checker to verify the solution instead of using diff.
I never really needed it, so never wrote one else i would have definitely updated the script.
Hey, I downloaded the ubuntu subsystem on Windows 10 and I tried to run this script. It gave an error like this -
root@LAPTOP-PFCO296F:/mnt/e/Stress-Testing-bash-script-master# bash s.sh
s.sh: line 12: g++: command not found Compilation Error in gen.cpp
I use g++ 9.2.0 but still this error. Any way around this? Any help is appreciated!
Its probably saying that you dont have g++, try running g++ --version once there, it should show the version if its successful
I didn't realize I had to install g++ in Ubuntu too. How stupid. Now it works. Thank You!
zass hey did it work after installing g++ like do i need to set path again i mean how to install g++ in ubuntu too ?? we already installed it right for normal ide i mean ...please tell me
In case someone was looking for a stress testing script with a checker, I found this blog pretty useful.