We will hold AtCoder Beginner Contest 163.
- Contest URL: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc163
- Start Time: http://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/fixedtime.html?iso=20200419T2100&p1=248
- Duration: 100 minutes
- Number of Tasks: 6
- Writer: gazelle, kyopro_friends, nuip, latte0119, ynymxiaolongbao, yuma000
- Rated range: ~ 1999
The point values will be 100-200-300-400-500-600.
We are looking forward to your participation!










Cannot access problems!!!
Click "tasks for printing" or here: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc163/tasks_print, works for me even though the individual problem pages don't.
Can't see the problem statements. :(
Edit — Unrated. F
For the first 4 minutes, it just was giving Error 502, bad gateway, and now it is loading the problem but all I see is an area to submit code, the text of the task itself is invisible!!
Atleast they should make an announcement about how much delay to expect or something regarding to this.
Can't see the problem statements only submit code is visible.
contest is unrated .
If someone wants to see the statements, press Ctrl + U and scroll the page down to the problem statement.
What does 'internal error' mean?
Submit again it will give AC now!!
It's AC now. your submissions
Looks Like Atcoder is getting Inspired By CF
Is the contest Unrated?
yes
Yes. I'm unhappy to hear that because I solved 4 problems with penalty 27:58 and got the 1017 place. (;′⌒`)
scalability issue
When E has more solver than A
orz first solver
Actually, I didn't know that for a while, and after the contest become unrated, I saw it by chance. Because the page of problem A was not displayed I solved B first, and that was lucky. :)
How to solve D-F?
+1
The solution for problem D: Sum of Large Numbers — here
Good. Thanks a lot!
my submission (problem D)
Video Tutorials for D and E
How to solve E?
Sort the children according to the Ai(from big to small)
Then if you are considering the i-th child,this is always arranged in the smallest position (aren't used) or the biggest position (aren't used) .
So we can dp.dp[i][j]means when considering the i-th child ,there are j children in the left ,the best answer.
We can update it easily.
UPDATE :SEARCH "Gary" in atcoder for the submission
Can you explain dp transitions?
For the ith element after sorting, you need to place it in the front or at the back. And at this time (i — 1), elements have already been placed. L of them are in the front and R of them are at the back. Here L + R = i — 1.
Then the dp transition is
Here pos[i] is the original position of the ith element, val[i] is its val.
why not take the maximum distance for given Ai either front or back
This was my doubt too. We are claiming to put the unassigned largest element at one of the extremes (I am guessing by thinking greedily?), then why not assign it to the farthest extremes. Can someone please clarify this?
That was my thought during the contest... But I guess one problem is : what do you do in case of equality ? If both extremes are of same distance to the current biggest element ? What extreme do you choose ?
It's not an obvious question and the DP array allows you to see what happens to both extremes.
Same thought came afterwards
Can you please prove why are we sorting in descending order.Gary2005
If Ai>Aj!
if i-th children and the j-th both move to the left,and the new j-th child's position is smaller.
There are two cases
we can describe them in the picture below.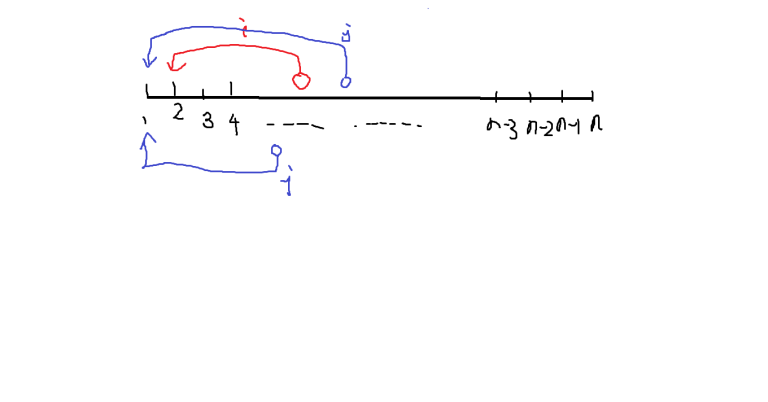 You can find that ,if the i-th moves to '1',and j-th moves to '2' ,the answer will be better.
You can find that ,if the i-th moves to '1',and j-th moves to '2' ,the answer will be better.
You can prove the case that i-th ,j-th both move to right like this.
Update: if we sort them in decreasing order we can consider the i-th earlier. So the situation above won't happen.
Thanks a lot for such a clear explanation
How to solve F?
see HDU 6035 Colorful Tree, after erasing all nodes of color u, find all connected components of the remaining tree and minus the num of paths without passing color u. We can do it by using tree DP like the problem above in $$$O(n)$$$
Thanks a lot ^_^
My thought is also in the same lines as yours.can you please quote some references for the dynamic programming part. Finding it difficult to think.
I have solved this problem using dp.
And the code is short and easy to understand.
Thank you.
can you please explain your solution.Gary2005
I want to share my dumb solution. For a color with $$$M$$$ vertice, we can build a virtual tree containing the $$$M$$$ vertice in $$$O(M \log M)$$$. (Don't know if we can do better) Then simply DFS the virtual tree and calculate the number $$$K$$$ of paths in the original graph that doesn't contain the vertex in virtual tree. Te answer for that color is $$$\frac{n (n + 1)}{2} - K$$$.
UPD: turns out it can be done in $$$O(M)$$$ since we don't need sorting in the problem code
Thank you.
I don't know if it was just me, but the website had full functionality in Firefox and not Chrome for the duration of the contest.
true
It's not about the particular browser as far as I understand Some of the responses from the server were cached in the browser during the heavy problems in the beginning. When you tried a different browser, it didn't have the same caches, so it worked fine. But you could just as well refresh the site ignoring the cache or reset it manually (ctrl-shift-R for me)
Is E maximum weighted bipartite matching problem. I have heard of the algorithm but don't know the algorithm.
I need help for problem D. Somebody help me! Why I got WA? here is the code.
There is no need to mod in sigma and rsigma.
Oh, I see. I thought that it can't change the result because the property of modular arithmetic (a — b) % c == (a % c — b % c) % c. Could you elaborate on that?
If you use mod in sigma and rsigma, the return value of rsigma maybe less than sigma, then you will get a negative number to add.
https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc163/submissions/12138480
This is my code for the problem. spookywooky has given the explanation for the problem.
For D the key observation is, that for any set of $$$k$$$ choosen numbers, we can build any sum in the interval from smallest possible to the biggest possible.
And those both numbers can be calculated in $$$O(1)$$$, so we can calculate the sum in $$$O(n)$$$.
Min sum for $$$k$$$ of $$$n$$$ is $$$((i-1)\cdot i)/2$$$
Max sum for $$$k$$$ of $$$n$$$ is $$$n\cdot i - ((i-1)\cdot i)/2$$$
$$$ans=\sum\limits_{i=k}^{n+1}{max(i)-min(i)+1}$$$
Can you tell why is max sum n*i — (i(i-1))/2. Like how a proof for that. Thanks :)
we choose k numbers from (n+1) numbers (0, 1, ..., n). The min is 0 + 1 + ... + k — 1 = (k — 1) * k / 2 The max is n + (n — 1) + ... + (n — (k — 1)) = (2n — k + 1) * k / 2
That's simple. Take sum as (n-i+1)+(n-i+2)+....(n-i+i) --> the largest i elements. That will give you (n.i)-(i(i-1)/2).
Can someone explain the recurrence and DP transitions in E?
I'll assume you already know that we should process the children from the biggest Ai first.
Define dp[l][r] as the maximum happiness we can get if we want to put the remaining children to index l to r. The answer will be dp[1][N]. If the current state is (l, r), that means we are currently processing child with index i = N — (r — l + 1) + 1. We will have two choices, either put this child to index l or index r. If we put it to index l, then the happiness will be abs(l — child_initial_position) * A + dp[l + 1][r]. If we put it to index r, then the happiness will be abs(r — child_initial_position) * A + dp[l][r — 1]. We will take the maximum of those. Hope it helps.
how to be sure that maximum element should be in corners only?
You can use exchange argument technique to proof it.
I am not really sure that my proof is correct, so I'll leave your question to someone more experienced.
What's exchange arguement technique. And can't E be done using maximum bipartitte matching.
That's my question too?
By rearrangement inequality, we can prove that, biggest element has to be multiplied with the biggest difference, which is possible only if we consider either extremes as its new position.
Thanks a lot for that explaination. Was really confused about this!
You can have a look at the English commentary of Problem E here.
take the sample 1 3 4 2 as example, the impact of every element in array should like this: [0, 1, 2, 3] [3, 0, 3, 6] [8, 4, 0, 4] [6, 4, 2, 0] it is easy to know that for every element, the impact of it is increasing whit itself like the element 4, the position is 3 then the effect of position of 4, 2, 1 is 4, 4, 8
now you can see that like two element ai and aj, ai>aj, both ai and aj wants position k, we need to put ai at k because: first put all ai and aj to k: (ai*(k-x))+(aj*(k-y)) now we need to move one to k-1 because just one can put to k, if we move ai we need minus ai, move aj we need minus aj, because ai>aj, so put ai at k is better.
O(1) Solution for Problem D
Can you tell me how you got this?
Here is Explanation for the Formula
Because all numbers between
and
(inclusive) are reachable.
What am I doing wrong in Problem D? code
In my code, for sample case-1,
ind = 0 1 2 3pre = 0 1 3 6suf = 6 6 5 3sum += (5-1+1) + (6-3+1) + (6-6+1) = 10I am just calculating min and max sum using prefix and suffix sums, but this approach isn't working for sample case-3.
In principle this is correct. There must be some of by one error, maybe caused by the fact that the first element in the set is 0.
mod=1e9+7.check it once
What's wrong?I can't see the statement!
Try using the tasks for printing feature: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc163/tasks_print
Can someone tell how to solve F?
Is this problem C? https://mirror.codeforces.com/problemset/problem/115/A
Similar problem statement, but not same. In atcoder C, we just had to print the frequencies.
I finally passed a solution for F (in 1829 ms)!
I realized the obvious technique of counting the sizes of the regions between two colors, doing the N*(N+1)/2 trick, and then complementary counting.
However, my implementation was really messy (main code was nearly 200 lines long!).
I ended up doing a pre-order traversal, and keeping track of a Binary Indexed Tree for each color. Any other ideas?