Let your spirit soar and have a joy-filled new year by playing Ghenshin :D
However, before that, I will recommend to you an interesting "Genshin Geometry" problem
(Problem F from the GYM The 2021 ICPC Asia Nanjing Regional Contest (XXII Open Cup, Grand Prix of Nanjing)).
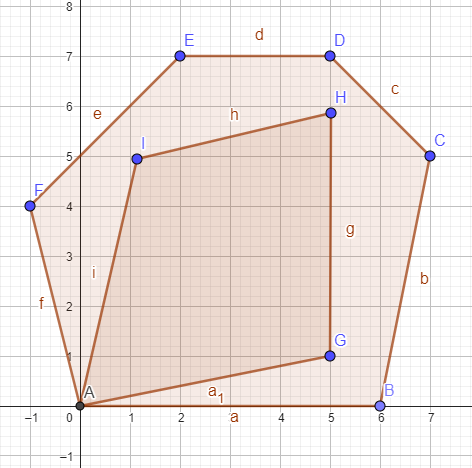
Summary: Give N distint points on the plane, and special point O = (0, 0). Your task is dividing this N points into two sets A and B so that:
Both of them is a strict convex set.
The outlines(edge) of two convex hulls only intersect at point O.
The sum of the perimeters of these two convex hulls is maximum.
So now, let's try to solve this problem by yourself...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
....before reading some hints!
Firstly, let's answer this question: Is there any TRICKS to contruct these two sets optimally directly ?. (It becomes a Greedy problem!!!). In my opinion, this problem has a lot of cases, and the greedy solution is difficult to approach. So, I will representation a general solution, but if you have a more optimal solution, please leave your commend and everyone can reference.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
struct point {
int x, y, index;
bool joined, isfault;
point() {}
point(int a, int b) {
x = a, y = b;
}
bool operator < (point other) {
return y < other.y || (y == other.y && x < other.x);
}
bool onSegment(point a, point b) {
if (ccw(a, b) != 0) {
return false;
}
int minx = min(a.x, b.x);
int maxx = max(a.x, b.x);
int miny = min(a.y, b.y);
int maxy = max(a.y, b.y);
return minx <= x && x <= maxx && miny <= y && y <= maxy;
}
int updown() {
if (y < 0 || (y == 0 && x > 0)) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int ccw(point a, point b) {
ll c = (ll)x * (a.y - b.y) + (ll)a.x * (b.y - y) + (ll)b.x * (y - a.y);
if (c == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (c > 0) {
return 1;
}
return - 1;
}
ld dist(point other) {
return hypot(x - other.x, y - other.y);
}
};
point O = point(0, 0);
bool cmp(point a, point b) {
if (a.updown() != b.updown()) {
return a.updown() < b.updown();
}
return (ll)a.y * b.x < (ll)a.x * b.y;
}
vector <point> Build_ConvexHull(vector <point> &p) {
vector <point> ans;
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
bool checking = true;
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) {
if (p[0].ccw(p[1], p[i]) != 0) {
checking = false;
break;
}
}
if (checking == true) {
ans = p;
p.clear();
return ans;
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) {
p[i].index = i;
p[i].joined = false;
}
vector <point> pts = p;
int n = p.size(), sz = 0;
p.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (i == n - 1 || pts[0].ccw(pts[i], pts[n - 1]) >= 0) {
while (sz > 0 && p[sz - 1].ccw(p[sz], pts[i]) < 0) {
sz--;
}
p[++sz] = pts[i];
}
}
if (sz != n - 1) {
for (int i = n - 2, j = sz; i >= 0; --i) {
if (i == 0 || pts[n - 1].ccw(pts[i], pts[0]) >= 0) {
while (sz > j && p[sz - 1].ccw(p[sz], pts[i]) < 0) {
sz--;
}
p[++sz] = pts[i];
}
}
p.resize(sz);
}
else {
p.resize(sz + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) {
pts[p[i].index].joined = true;
}
ans = p;
p.clear();
for (auto i : pts) {
if (i.joined == false) {
p.push_back(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ios_base :: sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
if (fopen("test.inp", "r")) {
freopen("test.inp", "r", stdin);
freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
}
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector <point> p(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
vector <point> points = p;
p.push_back(O);
ld ans = 0;
vector <vector <point>> pp(2);
pp[0] = Build_ConvexHull(p);
p.push_back(O);
pp[1] = Build_ConvexHull(p);
if (pp[0].size() + pp[1].size() == n + 2) {
bool checking = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
if (pp[i].size() < 3) {
checking = false;
break;
}
bool contain = false;
for (int j = 0; j < pp[i].size(); ++j) {
if (pp[i][j].x == 0 && pp[i][j].y == 0) {
contain = true;
}
int pre = (j - 1 + pp[i].size()) % pp[i].size();
int nxt = (j + 1) % pp[i].size();
if (pp[i][pre].ccw(pp[i][j], pp[i][nxt]) == 0) {
checking = false;
break;
}
}
if (contain == false) {
checking = false;
}
if (checking == false) {
break;
}
}
if (checking == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < pp[i].size(); ++j) {
int nxt = (j + 1) % pp[i].size();
ans += pp[i][j].dist(pp[i][nxt]);
}
}
}
}
p = points;
sort(p.begin(), p.end(), cmp);
int pos = - 1;
bool checking = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int nxt = (i + 1) % n;
if (p[i].onSegment(O, p[nxt]) || p[nxt].onSegment(O, p[i])) {
checking = false;
break;
}
}
if (checking == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int pre = (i - 1 + n) % n;
int nxt = (i + 1) % n;
if (p[pre].ccw(p[i], p[nxt]) < 0 || p[i].onSegment(p[pre], p[nxt])) {
p[i].isfault = true;
}
else {
p[i].isfault = false;
}
p[i].index = i;
}
vector <deque <point>> pts(2);
vector <ld> len(2, 0);
vector <int> fault(2);
vector <bool> status(2, true);
pts[0].push_back(p[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (p[0].ccw(O, p[i]) < 0) {
len[0] += pts[0].back().dist(p[i]);
if (pts[0].size() >= 2 && pts[0].back().isfault == true) {
status[0] = false;
fault[0] = pts[0].back().index;
}
pts[0].push_back(p[i]);
}
else {
if (pts[1].size()) {
len[1] += pts[1].back().dist(p[i]);
}
if (pts[1].size() >= 2 && pts[1].back().isfault == true) {
status[1] = false;
fault[1] = pts[1].back().index;
}
pts[1].push_back(p[i]);
}
}
if ((status[0] && pts[0].size() >= 2 && O.ccw(pts[0].front(), pts[0].back()) > 0) && (status[1] && pts[1].size() >= 2 && O.ccw(pts[1].front(), pts[1].back()) > 0)) {
ans = max(ans, len[0] + O.dist(pts[0].front()) + O.dist(pts[0].back()) + len[1] + O.dist(pts[1].front()) + O.dist(pts[1].back()));
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
point curr = pts[0].front();
if (pts[1].size()) {
len[1] += pts[1].back().dist(curr);
}
if (pts[1].size() >= 2 && pts[1].back().isfault == true) {
status[1] = false;
fault[1] = pts[1].back().index;
}
pts[1].push_back(curr);
pts[0].pop_front();
if (pts[0].size()) {
len[0] -= pts[0].front().dist(curr);
if (status[0] == false) {
if (pts[0].front().isfault == true && pts[0].front().index == fault[0]) {
status[0] = true;
}
}
}
else {
pts[0].push_back(p[i]);
point curr = pts[1].front();
pts[1].pop_front();
if (pts[1].size()) {
len[1] -= pts[1].front().dist(curr);
if (status[1] == false) {
if (pts[1].front().isfault == true && pts[1].front().index == fault[1]) {
status[1] = true;
}
}
}
}
while (pts[1].size() > 0 && p[i].ccw(O, pts[1].front()) < 0) {
curr = pts[1].front();
len[0] += pts[0].back().dist(curr);
if (pts[0].size() >= 2 && pts[0].back().isfault == true) {
status[0] = false;
fault[0] = pts[0].back().index;
}
pts[0].push_back(curr);
pts[1].pop_front();
if (pts[1].size()) {
len[1] -= pts[1].front().dist(curr);
if (status[1] == false) {
if (pts[1].front().isfault == true && pts[1].front().index == fault[1]) {
status[1] = true;
}
}
}
}
if ((status[0] && pts[0].size() >= 2 && O.ccw(pts[0].front(), pts[0].back()) > 0) && (status[1] && pts[1].size() >= 2 && O.ccw(pts[1].front(), pts[1].back()) > 0)) {
ans = max(ans, len[0] + O.dist(pts[0].front()) + O.dist(pts[0].back()) + len[1] + O.dist(pts[1].front()) + O.dist(pts[1].back()));
}
}
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(10) << ans << "\n";
}
}
This problem has two general case. The first case is easier to approach: convex hull covers convex hull.
So, set A is the convex hull of N points , and there are M remaining points that do not lie on this convex hull. Obviously, these M points are belong to the set B. Note, we need to check if remaining M points is strict convex and don't forget to the point O.
But wait, is there any special cases?