A: 379A - Новогодние свечки
Пусть cura количество целых свеч, curb — количество прогоревших. Изначально cura = a, curb = 0, тогда после того как прогорят все cura свечек, к ответу прибавится cura , а curb + = cura, переделаем прогоревшие свечки в целые cura = curb / b 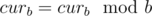 , будем повторять это пока мы можем сделать хотя бы одну целую свечу. #### B: 379B - Новогодний подарок Если в кошелек необходимо положить более одной монетки, то между операциями "положить монетку" можно передвинуться к соседнему кошельку, затем обратно. Так как почти на каждую операцию "положить монетку" мы будем тратить не более 2 дополнительных операции, легко проверить, что количество инструкций на максимальный тест не будет превышать 300 * 300 * 3 = 270000, что меньше 106.
, будем повторять это пока мы можем сделать хотя бы одну целую свечу. #### B: 379B - Новогодний подарок Если в кошелек необходимо положить более одной монетки, то между операциями "положить монетку" можно передвинуться к соседнему кошельку, затем обратно. Так как почти на каждую операцию "положить монетку" мы будем тратить не более 2 дополнительных операции, легко проверить, что количество инструкций на максимальный тест не будет превышать 300 * 300 * 3 = 270000, что меньше 106.
C: 379C - Новогоднее изменение рейтинга
Можно отсортировать рейтинги в порядке неубывания, затем итерируясь по ним можно поддерживать текущий минимальный рейтинг cur, который не был ни кому отдан. Тогда если ai > cur, i-му пользователю достанется ai рейтинга и cur = ai + 1, если ai ≤ cur то i-му пользователю достанется cur рейтинга и cur увеличится на единицу.
D: 379D - Новогоднее письмо
При честном моделировании, получения итоговой строки, мы столкнемся с проблемой того, что она достаточно велика. Заметим что для каждой итерации нам достаточно хранить количество подстрок AC в текущей строке, а также первую и последнюю буквы. Таким образом мы научимся быстро моделировать алгоритм для произвольных начальных строк. Единственное что нам осталось перебрать начальные строки, для этого воспользуемся алфавитом из трех букв A, C и любой другой на ваш вкус. Переберем первую и последнюю буквы строки, а также количество подстрок AC, которые у нас могу получится с такими начальной и последней буквой. Перебрав таким образом s1 и s2 мы сможем посчитать количество подстрок AC в sk.
E: 379E - Новогодние елочные украшения
Будем поддерживать объединение всех кусков до i-го, обозначим за S(i) площадь объединения первых i кусков. Тогда для того что бы узнать видимую площадь i-го куска нужно вычислить S(i) - S(i - 1), (S(0) = 0). Для простоты рассмотрим все отрезки с началом в x = 0 и концом в x = 1. Объединение будет представлять из себя выпуклую вниз ломанную, её можно представить как последовательность точек, каждая из которых соединена с соседней. Текущее объединение будет обновляться трапециями(часть куска). Понятно, что нам нужен будет только верхний отрезок, если он войдет в новое объединение тогда он должен будет пересечь два отрезка из объединения. Это пересечение мы можем найти за количество вершин в объединении, также каждый новый отрезок может добавить в объединение не более одной вершины. Если отрезок войдет в новое объединение то точки из объеденения, находящиеся под этим отрезком должны быть удалены. Таким образом количество вершин в объединении будет сравнимо с количеством кусков. Посчитав такие объединения для каждого сегмента, мы сможем получить ответ на задачу.
F: 379F - Новогоднее дерево
Скоро будет.
G: 379G - Новогодний кактус
На дереве эту задачу можно решать при помощи динамического программирования d[v][c][a], где v — номер вершины, c — тип этой вершины(чья игрушка висит или там не висит игрушек вовсе), a — количество игрушек в поддереве вершины v которые повесил Джек, само значение d[v][c][a] будет равно максимальному количеству игрушек, которые может повесить Джилл, при заданных условиях. Такую динамику можно считать перебирая сыновей вершины v и их тип и количество игрушек повешенных Джеком. Но у нас не дерево, а кактус, для того, что бы научиться решать эту задачу достаточно сжать циклы в кактусе в вершины тем самым получив обычное дерево, представив каждую вершину как последовательность вершин в цикле кактуса, из которых есть "продолжение" кактуса, и промежуточных вершин. Единственное что осталось, реализовать динамическое программирование на дереве, аккуратно обрабатывая каждую вершину.











problem A act optimally how to prove the algorithm acting optimmally ?
not really related to your question but actually a "brute-force" implementation can also AC 5571273 :)
edit : it's clearly optimal since make new candle when ever we can, it have the same idea with the tutorial but this may be easier to understand :p
maybe it's not a good question seems trivial I think maybe the candle which is run out and then make a new one have different choice of run out candle and run out ones may have different levels and maybe not using them all in the same time or in different order maybe different. your answer is implement not brute force or exhaustion.I may have consider all the situation .I`d like an elegant simple approach to the proof.
This Tutorial is too simple that I can't understand how to solve D after I read it : (
Look for example you need to calc s5 for strings s1 = CACACC and s2 = CACAA, represent s1 like 2 AC substring and first and last letter — CC,
s2 = (1, CA)
s3 = (3, CA) (AC + CC has no AC at the junction and we just take first and last letter)
s4 = (4 + 1, CA) (+1 because of at the junction substring AC appears)
s5 = (8 + 1, CA) (again).
I got it now.
yes, enough to sort out first and last letter and count of AC for s1, s2.
How can I obtain s1 and s2?
You could generate all strings using alphabet of 3 letters, important things in this strings would be first and last letter and amount of 'AC' substrings.
Great!
This tutorial' english gave me cancer XD
Any better explanation for problem E ?
Any better explanation for problem E ?
You can separate the problem into K parts, because each part is independent of the others. To solve for just one part, you can keep the segments (points) that builds it, at first there is only one segment, from (xk,0) to (xk+1,0) and the area is currently 0. For each new segment (each new decoration) we must build the parts again. To add a new segment Bk, you need to check for every segment Ak that builds the part with the new segment Bk:
(The y coordinate for the B segment means the y for the current x). After building the parts again you have the old ones and the new ones. The amount of area that they add to the answer of this decoration is the new area minus the old area. The overall idea is not hard, it is just can be tricky to implement, specially for those who don't have much geometry skills :) (like me). You can check my code here: 5594115
I have implemented an idea similar to yours ,can you have a look and tell me why it fails case 15? http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/379/submission/5597257
I have made some modifications to your code, but at the end what made it pass was adding an eps to the line intersection test: 5600093. I thought a while about it and made some test cases but couldn't come with an explanation why it is failing without that :/, does anyone know why would it fail?
Thanks,brunoja . I also managed to get a Happy New Year!'ed submission by adding epsilon comparison to the intersection test.
http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/379/submission/5597623
i thought that struct is faster than pair,but it seems not, i changed it to pair and got ac the C problem
What slowed you down wasn't struct, but the comparison function. See 5602813. I modified your comparison function and got AC, passing the arguments by reference and adding a "return false" at the end. Not sure why the latter is required but without it I got a WA in test #10.
hi! thank you soo much for your explanation! its very clear and now i know where my code is wrong! it seems that it cant handle the sort when the 2 values is same, and adding "return false" seems to fix it all! thank you very much once again!
You're welcome :)
pair<int,int> is basically the same as struct {int first, int second}; with some predefined comparison operators and constructors.
Problem G how to write O(N^2) dynamic solution for tree. O(N^3) is simple, but O(N^2) is not so obvious. Answer in Russian is also acceptable.
Hah, you will be surprised. O(n^2) is essentially exactly the same, but in vertex v you should not iterate a from 0 to n, but from 0 to size of subtree of v (it's obvious that a > size[v] makes no sense) which results in O(n^2) algorithm. Prove it by yourself, because it's very nice and remember that trick! This trick was used by Touma_Kazusa in his DP solution to http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/375/problem/E which was problem from last Tuesday :).
Nice thanks .I didn't know about it before.
Man, that's amazing! U made my day, really!
Can you share links to other problems, which demand using this trick to solve them? Thanks in advance.
http://main.edu.pl/en/archive/pa/2007/bar
Problem J from NCPC 2012 (it's not the only solution, but one of the possible) http://ncpc.idi.ntnu.no/ncpc2012/ncpc2012problems.pdf
Problem Pizzerias from Marathon24 qualifications (which I have prepared :P) http://www.marathon24.com/static/attachment/marathon24_piz_pl.pdf
Nice! Thanks again
This problem is a good example: 178F3 - Representative Sampling
Thank you!
Oh, I remember another one problem! In my opinion it's really brilliant, so here it goes: https://www.facebook.com/hackercup/problems.php?pid=413074315443326&round=499927843385312
Как автору в голову пришла идея задачи F?
Все задачи понравились. Особенно задача D. Автор молодец!
Can somebody, please, post at least a sketch of the actual solution on F? Thanks, Happy new year!
As someone already pointed out, this is the (almost) same problem: http://discuss.codechef.com/questions/24750/rrtree-editorial ;)
How to solve F?
http://mirror.codeforces.com/blog/entry/8929#comment-146418
How can I solve the problem F? Who can give me some idea? Thanks!
This is a problem about LCA?
Indeed, this is a problem about LCA. Let
end_firstandend_secondbe the endpoints of the diameter of the tree. When inserting an new nodeuwe first have to compute the2^j-thancestor ofu, for alljin range0..log2(N). After that, notice that a possibly new diameter may start fromjand end atend_first, or start atjand endend_second. So, you just compare the distances to get the new diameter, and you update properlyend_firstandend_second. I also have some code I wrote after the contest: http://mirror.codeforces.com/contest/379/submission/5603366. I hope this helps :)Thanks.My English is bad,but I still hope you can get gratitude from me!HaHa.
But I have another quetion now.When all nodes have two subtrees(except leaves),the height of a subtree is 1,another is [1,Q+1].In other words,the height of the new year tree is Q+2.Are you sure this solution will not be TLE?
Yes, because the complexity of the procedure
addis O(lgN), and the complexity of the procedurelcais also O(lgN). Both procedures are called2*Qtimes, so this gives us a total complexity of O(Q * lgN), which i think can easily pass all the system's tests. I hope I helped :)got the key.Thanks!
you can read more about LCA here https://community.topcoder.com/tc?module=Static&d1=tutorials&d2=lowestCommonAncestor I'am sure it'll help :D
got the key.Thanks!
coming soon after X years?
still coming soon, maybe next yr
10 years later and still nothing happens
How to solve the problem F with Centroid Decomposition
Задачу A можно ещё решить с помощью формулы: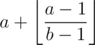
Задачу A можно ещё решить с помощью формулы: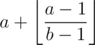
How to solve question B?
How to solve question F?